1. Introduction to Azure DevOps (ADO)
Azure DevOps (ADO) is Microsoft’s cloud-based DevOps platform that supports the entire software development lifecycle. It provides tools for:
- Project management (Boards & Backlogs)
- Source control (Repos)
- CI/CD pipelines (Pipelines & Releases)
- Testing tools (Test Plans)
- Monitoring & dashboards (Dashboards & Analytics)
For testers, Azure DevOps is especially useful for:
- Managing test plans, test suites, and test cases
- Linking tests with user stories or requirements
- Executing manual test runs
- Logging and tracking bugs
- Monitoring progress using dashboards and reports
2. Key ADO Modules for Testers
Boards
- Contains: Epics → Features → User Stories → Tasks → Bugs
- Testers commonly interact with User Stories and Bugs.
Test Plans
- Dedicated module for managing test assets.
Dashboards
- Used to track test progress, bug trends, upcoming tasks, etc.
3. Working With Test Plans
3.1 Creating a Test Plan
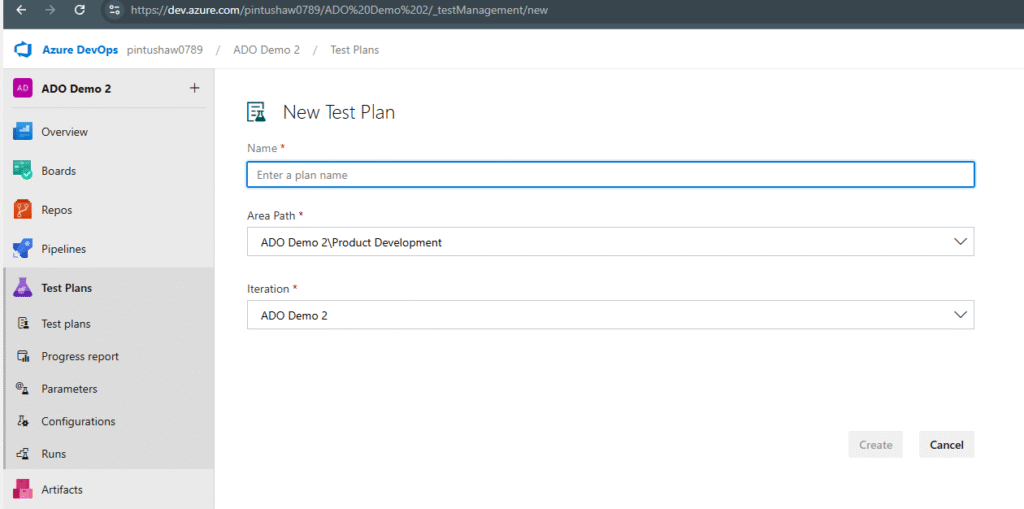
- Go to Azure DevOps → Test Plans.
- Click New Test Plan.
- Enter:
- Name (e.g., “Release 1.0 Test Plan”)
- Area Path (your team/project)
- Iteration Path (Sprint/Release)
- Click Create.
A Test Plan is the master container for organizing suites and test cases.
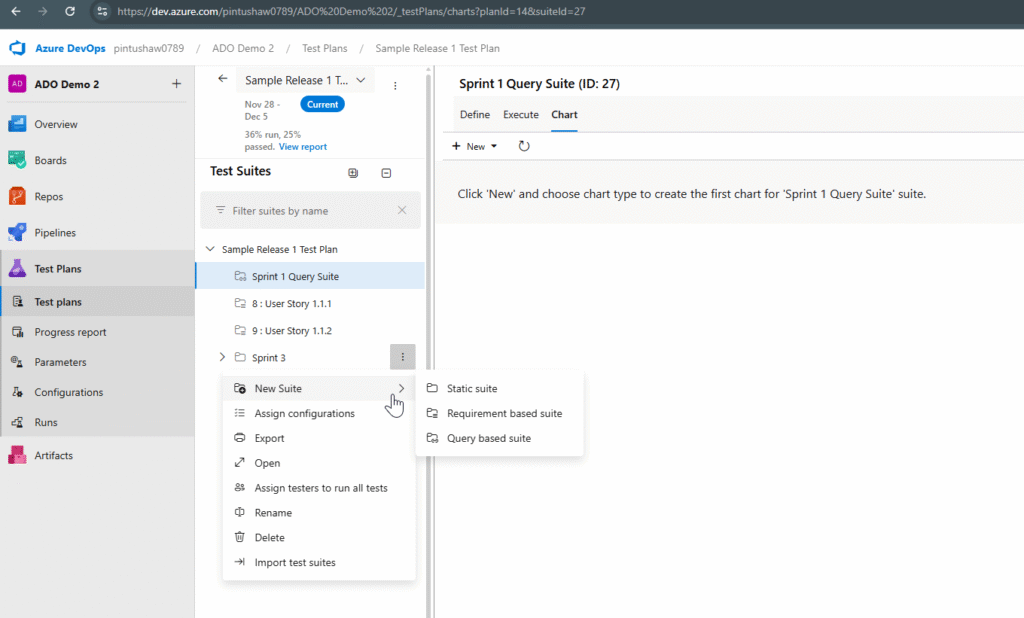
3.2 Creating Test Suites
Test suites organize test cases.
3 Types of Suites
- Static Suite – manually add test cases.
- Requirement-based Suite – automatically links to a User Story; pulls test cases tied to that story.
- Query-based Suite – pulls test cases based on a Work Item Query.
To Create a Suite:
- Within the Test Plan → click New → Test Suite.
- Choose the suite type.
- Name your suite (e.g., “Login Module”).
Recommendation: Use Requirement-based suites for linking tests directly with user stories.
4. Creating Test Cases
4.1 Creating a Test Case Inside a Test Suite
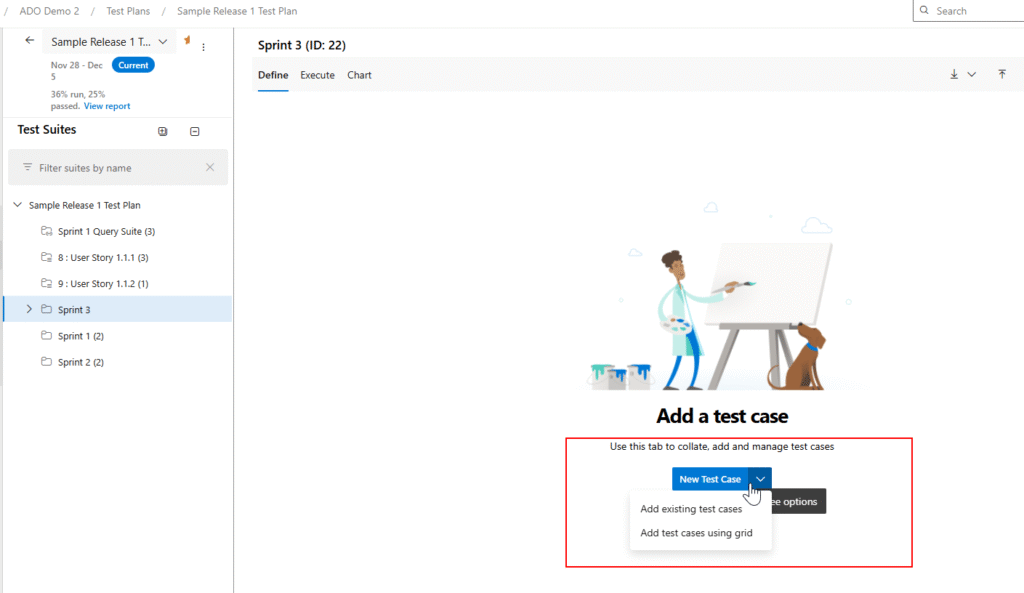
- Open a Test Suite.
- Click New Test Case.
- Fill the details:
- Title: Clear scenario name
- Steps:
- Action
- Expected Result
- Priority: P1/P2/P3 based on project rules
- Tags: Release/Sprint/Module tags
- Save & Close.
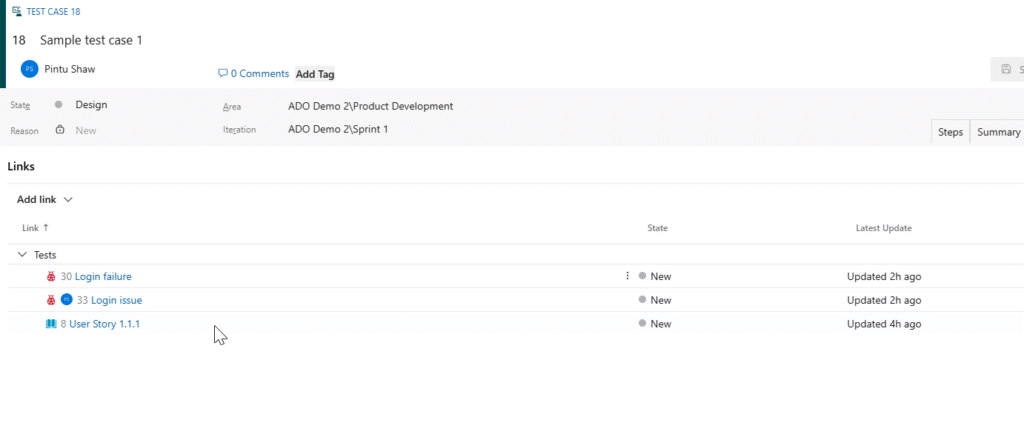
4.2 Linking Test Cases to User Stories
Linking ensures traceability from requirements → test cases → execution → results.
Method A: Using Requirement-Based Suites
- When you create a suite for a User Story, all test cases under that suite are auto-linked.
Method B: Manual Linking
- Open the Test Case → Links tab.
- Click Add Link → Related Work → Parent.
- Search for the User Story.
- Save.
5. Executing Test Cases
5.1 Running Test Cases
- Go to Test Plans → Test Suite.
- Select the test cases.
- Click Execute or Run for Web Application.
- A test runner window opens.
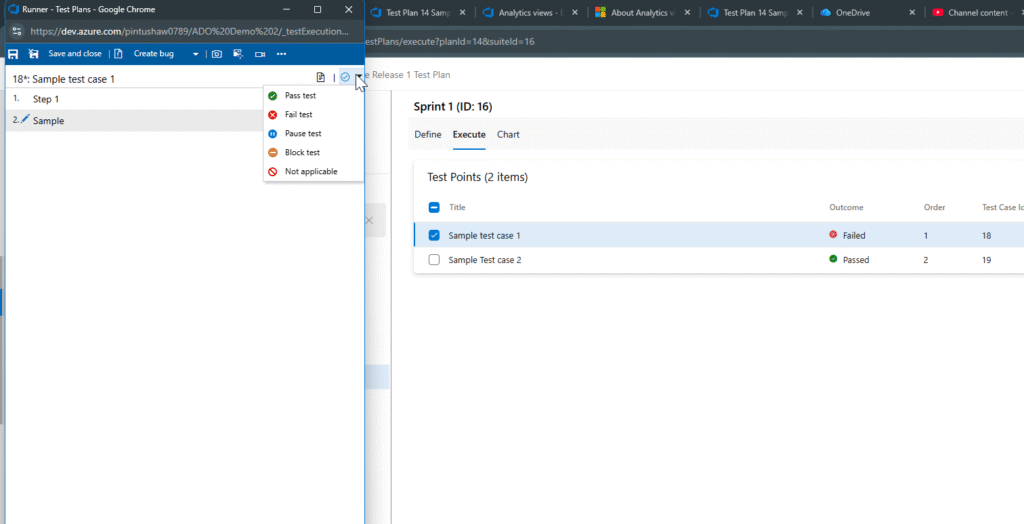
During Execution:
- Mark each step as:
- Passed
- Failed
- Blocked
- Not Applicable
- Add:
- Screenshots
- Attachments (logs, videos)
- Comments
At the end:
- Mark overall test case outcome
- Save & Complete execution
6. Logging Bugs During Test Execution
6.1 Logging a Bug Directly from Test Runner
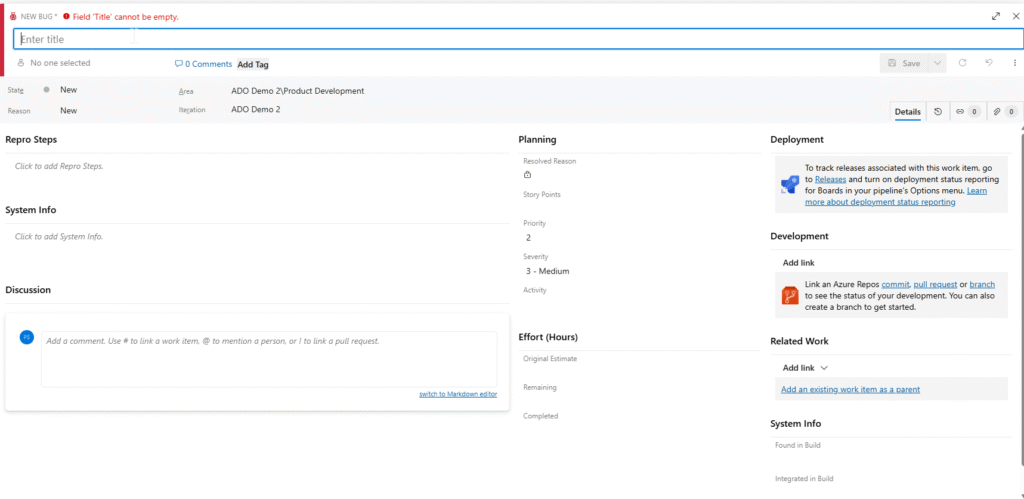
- In test runner window → when a step fails
- Click Create Bug
- A new bug form opens with:
- Step reproduction data auto-filled
- System/Browser version captured
- Screenshot from failure (if captured)
Fill Additional Fields:
- Title
- Area Path
- Severity
- Assigned To
- Tags (e.g., Regression, UI, Backend)
Click Save.
The failed test step automatically links the test case → test run → bug.
6.2 Logging a Bug Manually
- Go to Boards → Work Items → New Bug.
- Enter title, description, repro steps.
- Link to:
- Test Case
- User Story
- Task (optional)
- Save.
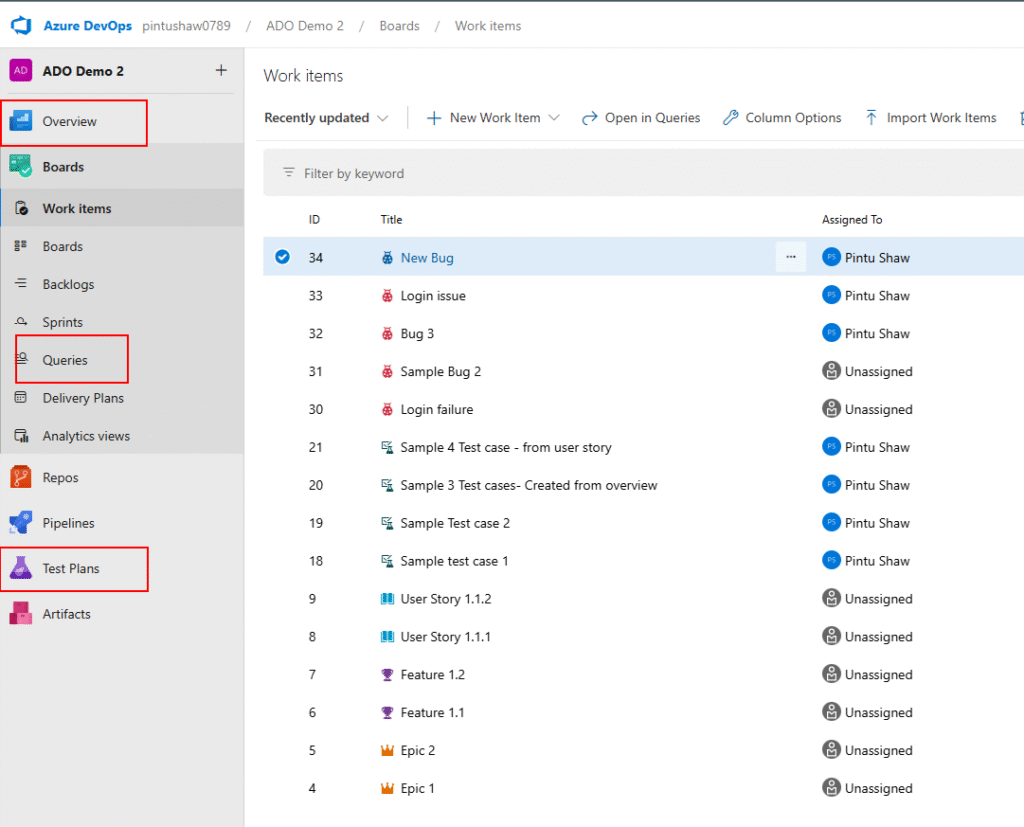
7. Queries
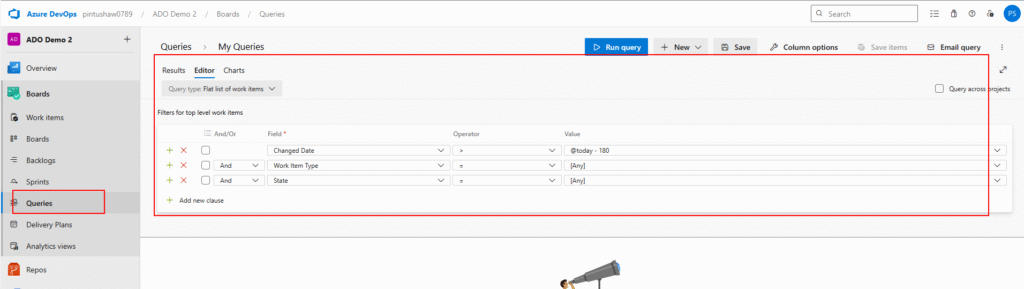
7.1 Creating a Query
- Navigate to Boards -> Queries
- Click New Queries
- Update the query conditions as per need
- Click on Save
- Enter Query name and folder and click OK
8. Tracking Test Progress and Reporting with Dashboards
8.1 Creating a Dashboard
- Navigate to Dashboards.
- Click New Dashboard.
- Enter name (e.g., “QA Status Dashboard”).
- Choose the team and layout.
- Create.

8.2 Useful Widgets for QA Tracking
Add widgets such as:
Testing
- Test Plan Progress
- Test Case Readiness
- Test Run Trend
- Test Results Chart
Bug Tracking
- Bug Trend (Past 30/60/90 days)
- Active Bugs
- Bugs by Severity/Priority
Sprint Overview
- Sprint Burndown
- Work Items by State
- Assigned Work Items
Analytics Views
(If Analytics extension is enabled)
- Test Failures Analytics
- Requirement Coverage
- Quality Trend
8.3 Creating Readable Charts
Use analytics-based reports for:
- Pass/Fail Ratio
- Test Execution Trend
- Defect Density per Module
- Defect Aging
These help track overall project quality and testing efficiency.
9. Best Practices for Testers Using ADO
Test Case Management
- Always link test cases to user stories for traceability.
- Keep test steps precise and actionable.
- Use consistent naming conventions.
Execution
- Capture evidence (screenshots/logs) for all failures.
- Mark test statuses accurately (avoid leaving them “not executed”).
Bug Management
- Write clear bug titles and repro steps.
- Set correct severity and priority.
- Link bugs to test cases and user stories.
Dashboards
- Update test cases before dashboards are auto-refreshed.
- Review dashboards daily during sprints.
10. Summary
This guide covers all essential Azure DevOps testing activities:
- Understanding ADO
- Creating Test Plans, Test Suites, Test Cases
- Linking with User Stories
- Executing test cases and logging bugs
- Building dashboards to track testing progress
Testers can use Azure DevOps as a single platform to ensure full visibility, end-to-end traceability, and better collaboration within development teams.
Use the below video for more details.
